CNN premarket futures provide crucial insights into potential market movements before the official opening bell. Understanding this data allows investors to anticipate trends, adjust strategies, and potentially gain an edge in the market. This guide delves into the sources, interpretation, and implications of CNN’s premarket futures reporting, equipping readers with the knowledge to navigate this dynamic aspect of financial markets effectively.
We will explore the various futures contracts covered, the reliability of CNN’s data sources, and the impact of economic indicators on premarket activity. Furthermore, we’ll examine practical strategies for interpreting data, managing risk, and leveraging premarket information for informed trading decisions. The goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of how to utilize CNN premarket futures data responsibly and effectively.
Understanding CNN Premarket Futures Data
CNN premarket futures data provides investors with valuable insights into the likely direction of various financial markets before the official opening of exchanges. This information, gleaned from trading activity during the premarket hours, can influence trading decisions and offer a glimpse into the potential market sentiment for the upcoming trading day. Understanding this data is crucial for informed investment strategies.Premarket futures trading allows investors to speculate on the future price of various assets before the regular trading session begins.
This activity often reflects overnight news events, economic announcements, or shifts in global market dynamics. Analyzing this premarket activity can help investors gauge potential volatility and adjust their positions accordingly.
Types of Futures Contracts Covered
CNN’s premarket futures reporting encompasses a broad range of futures contracts, mirroring the diversity of the global financial markets. These contracts cover major indices, commodities, and currencies. The specific contracts reported will vary depending on market activity and news relevance. Examples include futures contracts on the S&P 500 index (indicative of US large-cap equities), the Dow Jones Industrial Average (another key US equity index), crude oil (a major commodity), gold (a precious metal and safe haven asset), and currency pairs such as EUR/USD (Euro versus US Dollar).
The inclusion of these various asset classes allows for a comprehensive overview of anticipated market movements.
Information Included in CNN Premarket Futures Reports
CNN premarket futures reports typically provide concise and easily digestible information to aid investors in their decision-making. The data is presented in a clear and structured format, emphasizing key metrics that highlight price changes and trading volume. This allows for a rapid assessment of market sentiment and potential trading opportunities.
Key Data Points in CNN Premarket Futures Reports
| Data Point | Description | Example | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Futures Contract | The specific contract being traded (e.g., E-mini S&P 500). | ESZ24 (December 2024 E-mini S&P 500) | Identifies the underlying asset and expiration date. |
| Last Price | The most recent price at which the futures contract traded. | 4500 | Shows the current market value of the contract. |
| Change | The difference between the last price and the previous day’s closing price. | +25 | Indicates the direction and magnitude of price movement. |
| % Change | The percentage change in price relative to the previous day’s closing price. | +0.56% | Provides a standardized measure of price movement. |
Sources and Reliability of CNN Premarket Futures Data
CNN’s premarket futures data, like that of other financial news outlets, relies on a complex network of sources to provide viewers with timely and informative market insights before the official opening bell. Understanding these sources and their inherent limitations is crucial for interpreting the data accurately.The primary sources CNN utilizes for its premarket futures data include major global exchanges, such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME Group) and the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE), as well as data providers specializing in financial market information.
These providers aggregate data from various trading venues and utilize sophisticated algorithms to calculate and disseminate futures prices. The data feeds are typically real-time or near real-time, allowing for dynamic updates on CNN’s platforms.
Potential Biases and Limitations of CNN’s Premarket Futures Data
While CNN strives for accuracy, inherent biases and limitations exist within the premarket futures data they present. The data reflects the activity of a limited number of market participants active during the premarket hours. This segment of the market may not always be representative of the broader market sentiment and trading volume expected during regular trading hours. Furthermore, the data is susceptible to volatility and rapid changes due to overnight news events or global economic developments, potentially leading to temporary inaccuracies or misrepresentations of the actual opening price.
Another limitation is the potential for technical glitches or delays in data transmission, resulting in a brief lag between actual market activity and the data displayed on CNN.
Comparison with Other Financial News Sources
The reliability of CNN’s premarket futures data is comparable to that of other reputable financial news sources, such as Bloomberg, CNBC, and Reuters. All these sources rely on similar data feeds and methodologies, although slight variations in presentation and data aggregation techniques might lead to minor discrepancies in the displayed figures. However, significant differences are rare, and the overall reliability across these sources remains relatively high.
Differences are more likely to arise from the interpretation and presentation of the data, rather than from the underlying data itself. For instance, different news organizations might emphasize different aspects of the data, leading to different narratives.
Methodology for Presenting and Updating Premarket Futures Information
CNN employs a combination of automated data feeds and human oversight to present and update premarket futures information. Automated systems continuously pull data from their sources and display it in a user-friendly format, often including charts and graphs to visualize price movements. Human editors and analysts, however, play a vital role in verifying data accuracy, providing context, and interpreting potential market implications.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about cruise critic forum.
They ensure the information presented is clear, accurate, and free from significant errors. This combination of automated systems and human oversight helps maintain the integrity and reliability of the data displayed.
Interpreting Premarket Futures Movements
Premarket futures trading provides valuable insights into potential market direction before the official opening bell. Analyzing these movements allows investors and traders to anticipate potential price shifts and adjust their strategies accordingly. While not a perfect predictor, premarket activity often offers a strong indication of the overall sentiment and potential volatility expected during the regular trading session.Premarket futures movements reflect the collective expectations of market participants based on overnight news, economic data releases, and global events.
Significant upward or downward movements can signal a strong bullish or bearish sentiment, respectively, that is likely to carry over into the regular trading session. The magnitude of these movements can also be indicative of the potential for volatility throughout the day. For example, a large premarket drop might suggest a volatile opening with significant selling pressure.
Premarket Futures Impact on the Opening Bell
Significant premarket futures changes frequently influence the opening bell price and the subsequent trading session’s direction. For instance, if the S&P 500 futures contract experiences a substantial drop overnight, the market is likely to open lower. The degree of the opening gap, however, is not always directly proportional to the premarket movement; other factors such as order flow and algorithmic trading can play a role.
Consider the example of a major geopolitical event announced after the close of the previous day’s trading. If the news is overwhelmingly negative, futures contracts will likely reflect this sentiment during the premarket session. When the market opens, the price may gap down significantly, reflecting the premarket pessimism. Conversely, positive news can lead to a strong premarket rally and a higher opening price.
However, it’s crucial to remember that these relationships are not always linear; other factors can influence the opening price and the day’s overall trading dynamics.
Factors Influencing Premarket Futures Activity Beyond Domestic News
Premarket futures activity is not solely driven by domestic news. Global events, such as unexpected political developments in major economies or significant changes in currency exchange rates, can substantially impact futures prices. International economic data releases, such as unexpectedly strong or weak GDP growth figures from a major trading partner, can also significantly influence premarket trading. Furthermore, overnight trading in other global markets can set the tone for the US premarket session.
For example, a significant sell-off in the Asian markets overnight might create a negative sentiment that carries over to the US premarket and influences futures prices before the US market opens.
Hypothetical Scenario: Utilizing Premarket Futures in Trading Strategies
Imagine a scenario where a major technology company is expected to release earnings after the market close. In the premarket, the company’s stock futures contract is trading significantly higher than the previous day’s closing price. This suggests a positive market expectation regarding the earnings report. A trader could use this information to implement a strategy. They might consider placing a buy order at or slightly above the current premarket price, anticipating a further price increase upon the market’s open, based on the positive premarket sentiment.
Conversely, if the premarket shows a significant drop in the futures contract, the trader might choose to wait or even consider a short-selling strategy, depending on their risk tolerance and overall market outlook. This example demonstrates how premarket data can inform trading decisions and contribute to the development of more informed trading strategies. It is important to note that this is a hypothetical scenario, and actual market outcomes can vary significantly.
Thorough risk management is always crucial in any trading strategy.
Visualizing Premarket Futures Data: Cnn Premarket Futures
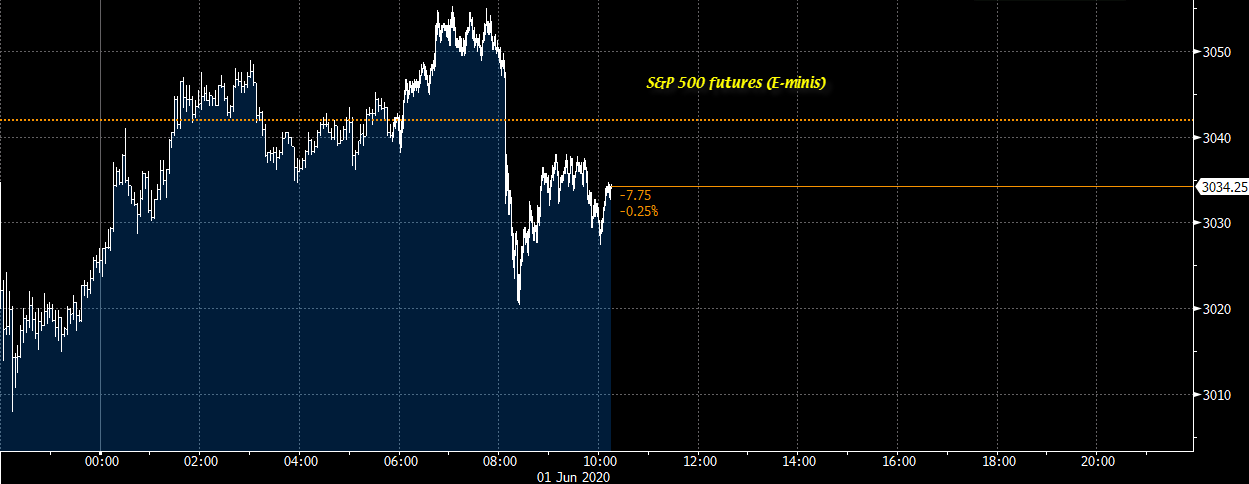
Premarket futures data visualization is crucial for understanding market sentiment and potential price movements before the regular trading session begins. Effective visualization techniques allow traders and investors to quickly identify trends, patterns, and potential risks. This section will explore various methods for visualizing this data and interpreting the resulting insights.
A Typical Premarket Futures Data Graph
A typical premarket futures data graph is usually a line chart or candlestick chart displaying the price of a futures contract over time. The horizontal axis represents time, typically displayed in hours and minutes, covering the premarket trading period (e.g., from 4:00 AM to 9:30 AM ET for US markets). The vertical axis represents the price of the futures contract, showing the price fluctuations during the premarket hours.
Data points are plotted at regular intervals, representing the price at each specific time. Trends are easily observed; an upward sloping line indicates an increase in price, while a downward sloping line indicates a decrease. Significant price changes or volatility are clearly visible as steeper slopes or sharp price spikes. For example, a sharp upward spike might indicate positive news or strong buying pressure.
Comparative Analysis of Premarket Futures Data Across Asset Classes
Comparing premarket futures data across different asset classes (e.g., indices like the S&P 500, individual stocks, commodities like gold or oil, and currencies) reveals correlations and divergences in market sentiment. This comparison can be achieved through multiple line charts displayed on the same graph, with each line representing a different asset class. This allows for a visual assessment of which asset classes are exhibiting similar or contrasting price movements.
For instance, a positive correlation might be observed between the S&P 500 futures and the Nasdaq futures, indicating a generally positive market sentiment. Conversely, a negative correlation between a specific stock’s futures and the overall market index futures could suggest company-specific negative news. Color-coding different asset classes enhances clarity and easy identification.
Interpreting Candlestick Patterns in Premarket Futures Charts, Cnn premarket futures
Candlestick charts provide a richer visual representation of premarket futures data, revealing information about price action and potential momentum. Each candlestick represents a specific time period (e.g., 15 minutes). The body of the candlestick shows the price range between the open and close, while the wicks (upper and lower shadows) show the high and low prices during that period. Common candlestick patterns, such as bullish engulfing patterns (a large green candlestick following a smaller red one, suggesting a potential price reversal), bearish engulfing patterns (the opposite), and doji (a candlestick with very small or no body, indicating indecision), can be identified to gain insights into potential future price movements.
However, it’s crucial to remember that these patterns are not foolproof predictors and should be used in conjunction with other forms of analysis. For example, a bullish engulfing pattern in the premarket might suggest a positive opening for the regular trading session.
Visual Representation of the Relationship Between Premarket Futures and Subsequent Market Performance
The relationship between premarket futures and subsequent market performance can be visualized using a scatter plot. The x-axis would represent the premarket price change (e.g., percentage change from the previous day’s close), and the y-axis would represent the corresponding change in price during the regular trading session. Each data point would represent a single trading day. A positive correlation would be shown by data points clustering around an upward-sloping line, indicating that positive premarket movements generally lead to positive regular session movements.
A weak correlation would show a more dispersed distribution of data points. This visualization helps assess the predictive power of premarket futures data and quantify the relationship between the two periods. Outliers can highlight instances where premarket movements did not accurately predict the subsequent market behavior, possibly due to unexpected news or events during the regular trading session.
Premarket Futures and Economic Indicators
Premarket futures, reflecting anticipated market movements before regular trading hours, are significantly influenced by economic indicators. Understanding this correlation allows investors to better interpret market sentiment and potentially anticipate market direction. The relationship is complex, however, and not all indicators hold equal weight.Premarket futures movements and key economic indicators exhibit a strong, albeit often indirect, relationship. The release of significant economic data frequently triggers immediate reactions in futures markets, reflecting investors’ assessments of the data’s implications for future economic growth, inflation, and monetary policy.
Influence of Key Economic Indicators on Premarket Futures
Several key economic indicators consistently demonstrate a strong influence on premarket futures. These include Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth, inflation data (as measured by the Consumer Price Index or CPI and Producer Price Index or PPI), employment figures (such as the Nonfarm Payrolls report), and interest rate decisions from central banks like the Federal Reserve. A strong GDP growth report, for instance, generally leads to increased optimism and higher futures prices, while unexpectedly high inflation often results in decreased futures prices as investors anticipate potential central bank intervention.
Conversely, disappointing employment data may signal a weakening economy, potentially leading to lower futures prices.
Examples of Economic News Releases Impacting Premarket Futures Trading
The release of the monthly Nonfarm Payrolls report is a prime example. If the reported number of jobs created significantly exceeds expectations, it often boosts premarket futures as it suggests a healthy economy. Conversely, a lower-than-expected figure can lead to a decline in futures prices, reflecting concerns about slower economic growth. Similarly, unexpected shifts in inflation data, such as a surprisingly high CPI reading, can trigger immediate sell-offs in premarket futures as investors anticipate potential interest rate hikes to combat inflation.
A surprise interest rate cut by the Federal Reserve, on the other hand, could cause a significant upward movement in premarket futures, reflecting increased investor confidence and expectations of improved economic conditions.
Predicting Economic Trends Using Premarket Futures Data
While premarket futures data cannot definitively predict future economic trends, they can offer valuable insights into market sentiment and potential shifts. Analyzing the reaction of futures markets to economic news releases can provide a real-time gauge of investor confidence and expectations. For example, a consistently strong positive reaction in premarket futures to positive economic news, coupled with a consistently negative reaction to negative news, might suggest a generally optimistic outlook among investors.
However, it’s crucial to remember that premarket futures are just one piece of the puzzle and should be considered alongside other economic indicators and fundamental analysis before making any investment decisions. Over-reliance on premarket movements alone can be risky, as these movements can be influenced by factors beyond pure economic fundamentals, such as news events unrelated to economic data, geopolitical tensions, or even technical trading patterns.
Mastering the interpretation of CNN premarket futures data offers a significant advantage in today’s fast-paced financial landscape. While not a crystal ball, understanding the underlying sources, potential biases, and correlation with economic indicators allows for more informed trading decisions and a proactive approach to risk management. By carefully considering the information presented, and combining it with other market analyses, traders can refine their strategies and navigate the complexities of the market with greater confidence.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Futures-19f64f0cf82148619e4d485cdb5b2c19.jpg)

