IPGrabber: Understanding this insidious tool requires exploring its various forms, methods, and the significant risks it poses. From simple scripts to sophisticated malware, IP grabbers exploit vulnerabilities to collect IP addresses for malicious purposes, ranging from targeted attacks to large-scale data breaches. This exploration delves into the technical aspects, detection methods, and legal ramifications associated with IP grabbers, offering a comprehensive understanding of this critical cybersecurity threat.
This examination will cover the diverse methods employed by IP grabbers, including techniques used to extract IP addresses from websites and applications. We will analyze the underlying vulnerabilities that allow these tools to operate, providing practical examples and code snippets (sanitized for illustrative purposes) to demonstrate their functionality. Furthermore, we will discuss effective countermeasures, prevention strategies, and the legal and ethical implications surrounding the creation and use of IP grabbers.
What is an IP Grabber?: Ipgrabber
An IP grabber is a piece of software or a script designed to identify and record the IP addresses of internet users. It functions by exploiting vulnerabilities in websites or applications, or by employing deceptive techniques to trick users into revealing their IP addresses. Understanding how IP grabbers work is crucial for protecting personal online privacy and security.IP grabbers come in various forms, each employing different methods to achieve their goal.
Their complexity ranges from simple scripts to sophisticated malware capable of extensive network surveillance. The methods used, and the potential for malicious use, vary significantly depending on the type of IP grabber.
Types of IP Grabbers
Several categories of IP grabbers exist, differentiated primarily by their methods of operation and target. These distinctions are crucial in understanding the potential threat level and the sophistication of the attack. A simple script embedded in a website is far less dangerous than a sophisticated piece of malware capable of persistent monitoring.
Methods Used to Obtain IP Addresses
IP grabbers utilize various techniques to extract IP addresses. These range from passive methods, such as analyzing HTTP headers, to active methods that involve exploiting vulnerabilities in web applications or tricking users into revealing their information. The sophistication of the method used often correlates with the level of malicious intent behind the IP grabber. For example, a simple script might only collect IP addresses from website visitors, while a more advanced program might actively scan networks for vulnerable devices.
Malicious Uses of IP Grabbers
The information gathered by IP grabbers can be misused in a variety of ways, often with serious consequences for the victims. The malicious use of this data ranges from relatively minor inconveniences to serious criminal activities. Understanding these potential uses is essential for developing effective security measures. For instance, an IP grabber might be used to target individuals for phishing attacks, DDoS attacks, or other forms of cybercrime.
The collected IP addresses could be used to identify the location of the users, allowing for targeted attacks based on geographic location. Furthermore, this data could be sold on the dark web, contributing to the growth of cybercrime marketplaces. The potential for abuse highlights the need for robust online security practices.
Obtain a comprehensive document about the application of tx time zone that is effective.
Detection and Prevention of IP Grabbers
Protecting yourself from IP grabbers requires vigilance and a proactive approach. Understanding the methods used by these malicious programs, and implementing appropriate preventative measures, is crucial to maintaining online security. This section will Artikel common indicators of an attack, methods for detection, and a comprehensive strategy for prevention.
Common Signs of an IP Grabber Attack
Suspicious activity is often a key indicator of an IP grabber attack. This might include unexpectedly high network traffic, particularly outbound connections to unfamiliar servers or IP addresses. Performance degradation on your network, such as slowdowns or application freezes, can also suggest malicious activity. Furthermore, unusual login attempts or unauthorized access to your accounts should raise serious concerns.
Finally, the presence of unknown or suspicious processes running on your system warrants investigation.
Methods for Detecting IP Grabbers on a Network, Ipgrabber
Network monitoring tools are essential for detecting IP grabbers. These tools can analyze network traffic patterns, identifying unusual or excessive outbound connections that might indicate a compromised system. Regular security scans, using both automated tools and manual inspections, are also vital. Analyzing system logs can reveal unauthorized access attempts or the execution of unknown processes. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) can provide real-time alerts about suspicious network activity.
Finally, employing a dedicated endpoint detection and response (EDR) solution can identify and respond to malicious activities directly on affected systems.
A Strategy for Preventing IP Grabber Attacks
A multi-layered approach is necessary for effective prevention. This includes regularly updating all software and operating systems to patch known vulnerabilities. Strong, unique passwords for all accounts are essential, and the use of multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds a significant layer of security. Educating users about phishing scams and social engineering tactics is crucial, as many IP grabbers are deployed through these methods.
Regular security audits and penetration testing can identify weaknesses in your network security posture. Implementing robust network segmentation can limit the impact of a successful attack. Finally, employing a well-configured firewall is a fundamental element of a comprehensive security strategy.
The Role of Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
Firewalls act as the first line of defense, blocking unauthorized access attempts and filtering malicious network traffic. They can be configured to block connections to known malicious IP addresses and prevent unauthorized outbound connections. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns and alert administrators to potential threats. They can detect attempts to exfiltrate data or unusual network scans that might indicate an IP grabber is active.
By working together, firewalls and IDS provide a robust security posture, significantly reducing the risk of successful IP grabber attacks.
Best Practices for Avoiding IP Grabber Attacks
To minimize the risk of falling victim to an IP grabber, consider the following best practices:
- Keep your software and operating systems updated with the latest security patches.
- Use strong, unique passwords for all online accounts and enable multi-factor authentication wherever possible.
- Be wary of suspicious emails, links, and attachments; avoid clicking on anything that seems questionable.
- Regularly back up your important data to prevent data loss in the event of an attack.
- Use reputable antivirus and anti-malware software and keep it updated.
- Educate yourself and your users about social engineering techniques and phishing scams.
- Regularly review network logs and security alerts for suspicious activity.
- Consider implementing a network intrusion detection and prevention system.
Legal and Ethical Implications

IP grabbers, while possessing legitimate applications, often tread a fine line between acceptable use and illegal activity. The legal and ethical ramifications depend heavily on the intent and application of the tool, with malicious use carrying severe consequences. Understanding these implications is crucial for anyone considering developing or utilizing IP grabbing techniques.
Legal Ramifications of Creating and Using IP Grabbers
The legality of creating and using IP grabbers varies significantly depending on jurisdiction and the specific purpose. Creating and distributing an IP grabber designed for malicious purposes, such as unauthorized network surveillance or launching cyberattacks, is illegal in most countries. This often falls under laws concerning computer crime, hacking, unauthorized access, and data theft. The penalties can be severe, including hefty fines and imprisonment.
Even using a readily available IP grabber for illegal activities exposes the user to prosecution. Conversely, developing an IP grabber for legitimate network monitoring purposes within a controlled environment, with explicit consent from all involved parties, is generally considered legal. However, even in such scenarios, it is crucial to comply with all relevant data privacy regulations.
Ethical Considerations Surrounding IP Grabbing
The ethical considerations surrounding IP grabbing are complex. While legitimate uses exist, the potential for misuse is significant. The fundamental ethical concern is the violation of privacy. Gathering someone’s IP address without their knowledge or consent is a breach of privacy, potentially leading to tracking, identification, and other forms of intrusion. Even in cases where IP grabbing is technically legal, ethical considerations mandate transparency and informed consent.
A responsible approach would involve clearly informing users about IP address collection, explaining the purpose, and obtaining explicit consent. Failure to do so raises serious ethical questions about respect for individual privacy and data security.
Comparison of Legitimate and Malicious Uses of IP Grabbers
Legitimate uses of IP grabbers are typically confined to network administration and security auditing within controlled environments. Network administrators might use IP grabbers to identify unauthorized devices on their network or troubleshoot connectivity issues. Security professionals may employ them to detect and analyze malicious activity. In these cases, consent is implied through the employee-employer relationship and adherence to internal policies.
In contrast, malicious use involves obtaining IP addresses without consent for purposes such as targeted attacks (DDoS, phishing), identity theft, or unauthorized surveillance. These actions violate privacy rights and can lead to significant harm. The key difference lies in the intent and the presence or absence of informed consent.
Real-World Cases Involving IP Grabbers and Their Legal Consequences
Several real-world cases highlight the legal consequences of IP grabbing. For instance, individuals who have developed and distributed malicious IP grabbers have faced criminal charges, resulting in substantial fines and prison sentences. Cases involving the use of IP grabbers in large-scale DDoS attacks have led to significant legal repercussions for the perpetrators. Furthermore, companies found using IP grabbers to illegally collect user data have faced lawsuits and regulatory penalties for violating privacy laws such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act).
The specific legal outcomes depend on the jurisdiction, the nature of the offense, and the extent of the damage caused. These cases underscore the importance of adhering to legal and ethical standards when dealing with IP grabbing technology.
Countermeasures and Mitigation Strategies
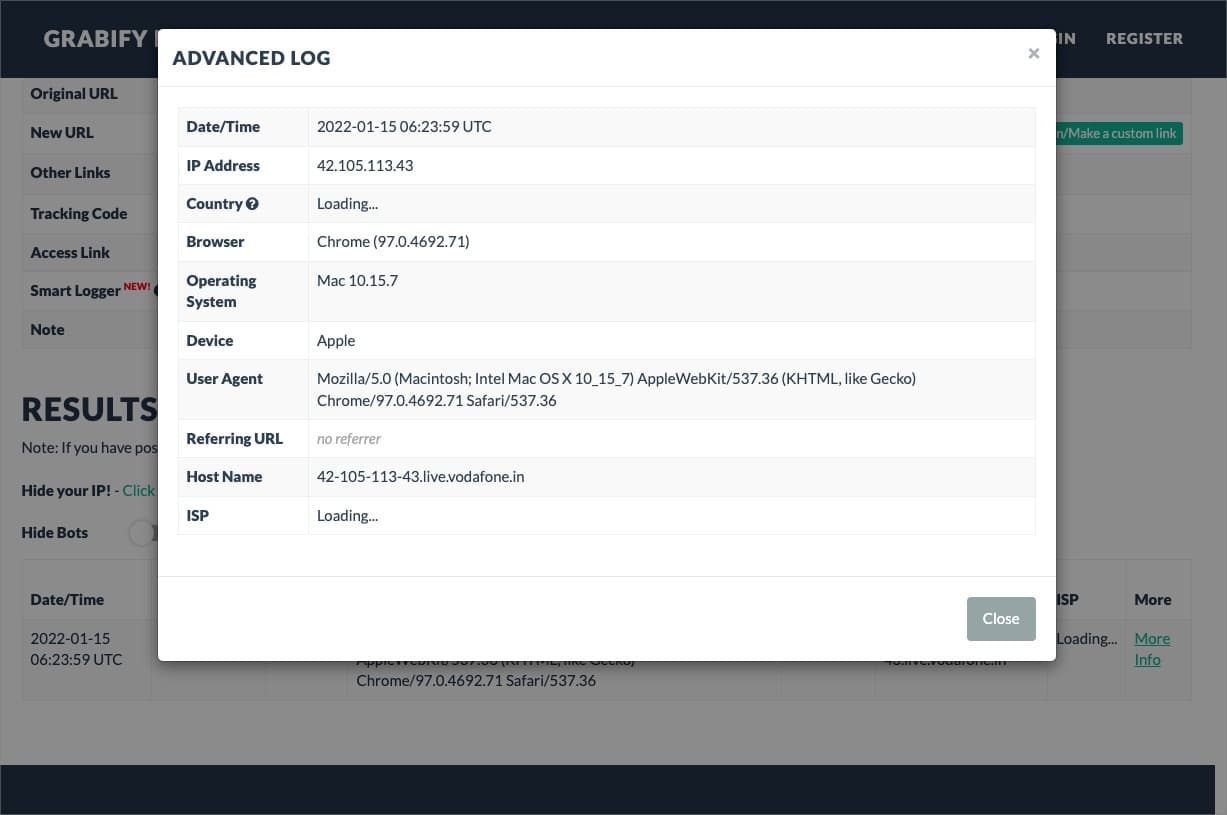
Protecting against IP grabbers requires a multi-layered approach encompassing proactive security measures and reactive incident response plans. A robust security posture minimizes vulnerabilities and limits the impact of successful attacks. Effective incident response ensures swift containment and minimizes potential damage.
A comprehensive strategy combines network security best practices with user education and awareness. Regular updates and patches are crucial, as are strong access controls and intrusion detection systems. Analyzing network traffic for suspicious activity is also essential for early detection and prevention.
Designing a Comprehensive Security Plan to Protect Against IP Grabber Attacks
A comprehensive security plan should address several key areas. Firstly, it necessitates regular software updates for all systems and applications to patch known vulnerabilities exploited by IP grabbers. Secondly, strong, unique passwords and multi-factor authentication should be mandatory for all user accounts. Thirdly, robust firewalls should filter incoming and outgoing traffic, blocking known malicious IP addresses and suspicious network activity.
Finally, implementing an intrusion detection and prevention system (IDPS) can help identify and block IP grabber attempts in real-time. Regular security audits and penetration testing further enhance the plan’s effectiveness by identifying weaknesses before attackers can exploit them. Employee training on recognizing and reporting phishing attempts and other social engineering tactics is also critical, as these are often the initial vectors for IP grabber deployment.
A Step-by-Step Guide for Responding to an IP Grabber Incident
Responding to an IP grabber incident requires a swift and organized approach. The first step involves isolating affected systems from the network to prevent further compromise and data exfiltration. Next, a thorough investigation is needed to identify the extent of the breach, including which systems were affected and what data may have been compromised. This typically involves analyzing system logs, network traffic, and potentially forensic analysis of affected machines.
Once the extent of the breach is understood, the compromised systems should be sanitized and reimaged. This involves completely wiping the systems and reinstalling the operating system and applications. Finally, a post-incident review should be conducted to identify weaknesses in the security posture that allowed the attack to occur and implement corrective measures to prevent future incidents.
Notification of affected parties, if necessary, should also be part of the response plan.
Analyzing Network Traffic to Identify Potential IP Grabbing Activity
Analyzing network traffic for potential IP grabbing activity requires careful examination of various data points. This includes looking for unusually high volumes of outgoing connections to unfamiliar servers, especially those located in countries known for malicious activity. Another key indicator is the presence of unusual DNS queries, which could indicate attempts to resolve malicious domains associated with IP grabbers.
Additionally, monitoring for suspicious network protocols and port usage, such as those commonly used by IP grabbers, is crucial. Using network monitoring tools with advanced features like deep packet inspection can help identify malicious payloads hidden within seemingly benign traffic. Analyzing logs from firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and web servers can also provide valuable insights into potential IP grabbing attempts.
Correlating data from multiple sources enhances the accuracy of detection.
Visual Representation of a Typical IP Grabber Attack Flow
Imagine a diagram showing a user visiting a compromised website. The website, unbeknownst to the user, contains malicious JavaScript code. This code, when executed in the user’s browser, establishes a connection to a remote server controlled by the attacker. This connection transmits the user’s IP address to the attacker’s server, which logs it for later use in malicious activities such as DDoS attacks, spam campaigns, or targeted phishing attempts.
The attack flow progresses from the user’s interaction with the compromised website to the data transmission and finally the storage of the IP address on the attacker’s server. The entire process is covert, often leaving no obvious traces on the user’s machine. The visual representation would clearly depict the stages of this attack, highlighting the user’s browser, the malicious website, the network connection, and the attacker’s server, demonstrating the data flow.
In conclusion, understanding IP grabbers is crucial for navigating the complex landscape of online security. This exploration has highlighted the various methods used, the vulnerabilities exploited, and the significant legal and ethical considerations involved. By implementing robust security measures, staying informed about emerging threats, and understanding the legal implications, individuals and organizations can effectively mitigate the risks associated with IP grabber attacks and maintain a secure online environment.
Proactive defense and a comprehensive understanding of this threat are key to minimizing vulnerability.


