LandWatch Map offers a powerful platform for accessing and analyzing diverse land data. This innovative tool provides users with detailed information ranging from property boundaries and land use to topography and environmental features, empowering informed decisions across various sectors. Its intuitive interface and robust data layers make it a valuable resource for real estate professionals, land managers, conservationists, and agricultural planners alike.
From pinpointing ideal property locations to assessing environmental impacts, LandWatch Map streamlines complex processes. The platform’s accuracy is ensured through rigorous data sourcing and verification methods, though users should be aware of potential limitations inherent in any geographic information system (GIS). This article delves into the map’s functionality, data accuracy, applications, user experience, and future development potential, offering a complete overview of this essential tool.
LandWatch Map Functionality
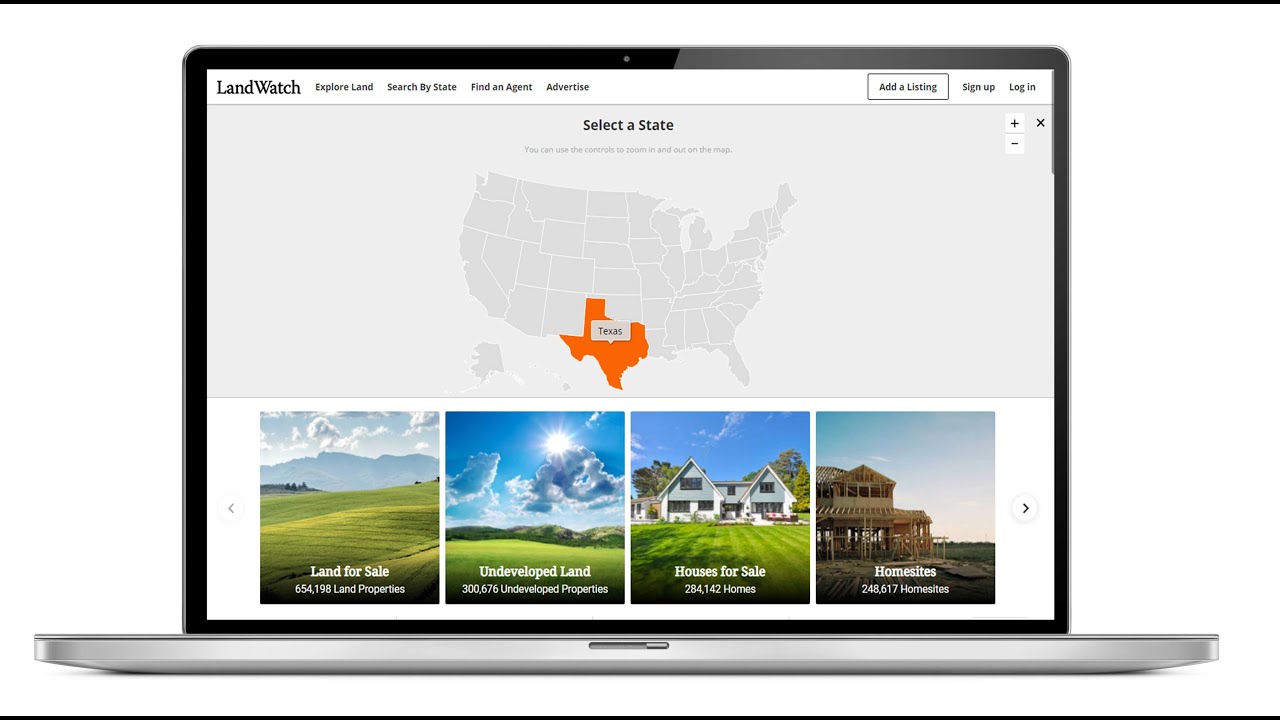
LandWatch maps provide a comprehensive platform for visualizing and interacting with land-related data. Its core functionality revolves around user-friendly navigation, detailed data layers, and powerful search tools. This allows users to efficiently explore and analyze land information for various purposes.
Core Features of LandWatch Maps
LandWatch maps offer a suite of core features designed for efficient land exploration and analysis. These include a powerful search engine allowing users to pinpoint specific properties based on various criteria, such as location, acreage, and property type. Interactive tools allow users to measure distances and areas, and the ability to download map data in various formats facilitates further analysis.
The map also features a customizable display, allowing users to toggle the visibility of different data layers according to their needs.
Data Layers Available on LandWatch Maps
LandWatch maps integrate multiple data layers to provide a holistic view of land characteristics. These layers include detailed property boundaries, clearly defining ownership limits. Land use information categorizes parcels based on their designated purpose (residential, agricultural, commercial, etc.). Topographical data provides elevation information, showcasing terrain features like hills, valleys, and waterways. Other potential layers might include soil type, vegetation cover, and infrastructure details like roads and utilities.
User Interaction and Navigation
Navigating LandWatch maps is intuitive and user-friendly. Users can pan and zoom using standard map controls, and a search bar facilitates quick location identification. The map employs a standard map interface with familiar tools and controls, such as zooming, panning, and layering, making it accessible to users with varying levels of technical expertise. Clear labeling and visual cues enhance navigation and data interpretation.
Step-by-Step Guide on Using LandWatch Map Tools for Property Searching
1. Access the LandWatch Map
Navigate to the LandWatch map website.
2. Enter Search Criteria
Utilize the search bar to specify location, property type, acreage, or other relevant parameters.
3. Refine Results
Employ filtering options to narrow down the search results based on specific requirements.
4. Analyze Results
Review the displayed properties, examining boundaries, land use, and other relevant data layers.
5. Select Property
Click on a property to view detailed information, including ownership details, and associated data.
Comparison of LandWatch Maps with Similar Mapping Services
| Feature | LandWatch Maps | Service A | Service B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Layers | Property boundaries, land use, topography, potentially soil type and infrastructure | Property boundaries, aerial imagery | Property boundaries, land use, zoning |
| Search Functionality | Advanced search with multiple criteria | Basic location-based search | Advanced search with filters |
| User Interface | Intuitive and user-friendly | Moderately user-friendly | Steep learning curve |
| Cost | [Insert pricing model] | [Insert pricing model] | [Insert pricing model] |
Data Sources and Accuracy
The accuracy and reliability of LandWatch maps depend heavily on the quality and precision of its data sources. Understanding these sources and their inherent limitations is crucial for responsible map interpretation.
Primary Data Sources
LandWatch maps likely draw data from a variety of sources, including publicly available GIS data from government agencies (e.g., county assessor’s offices, land surveying records), private surveying firms, and potentially satellite imagery. The specific sources will vary depending on the geographic area covered.
Methods for Ensuring Data Accuracy
Data accuracy is maintained through a combination of methods. Regular updates from source data providers are crucial. Quality control procedures, involving data validation and verification, help to identify and correct errors. User feedback mechanisms allow for the identification and correction of discrepancies.
Browse the implementation of listcrawler male in real-world situations to understand its applications.
Potential Limitations and Inaccuracies
Despite efforts to maintain accuracy, certain limitations exist. Data may be outdated, particularly in rapidly developing areas. The accuracy of boundary lines might vary due to the age or methodology of original surveys. Interpretation of land use classifications can also be subjective.
Comparison of Data Accuracy
Direct comparison of data accuracy with other services requires access to independent accuracy assessments of all platforms. However, general considerations include the age of data, source reliability, and update frequency. Governmental sources generally are considered to have higher accuracy than privately sourced data, however, that does not mean that there are no errors present.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Data Sources
| Data Source | Strengths | Weaknesses | Accuracy Level (General) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Governmental GIS Data | Generally reliable, publicly accessible | May be outdated, varying levels of detail across jurisdictions | High |
| Private Surveying Firms | High accuracy for specific surveys | Costly, limited geographic coverage | High to Medium |
| Satellite Imagery | Up-to-date visual information | Interpretation can be subjective, resolution limitations | Medium |
Note: Accuracy levels are general and can vary widely based on specific datasets and methodologies.
Applications and Use Cases: Landwatch Map
LandWatch maps find diverse applications across various sectors, facilitating informed decision-making in land-related activities.
Real Estate Transactions

LandWatch maps are invaluable in real estate transactions. Buyers and sellers can verify property boundaries, assess lot size, and analyze surrounding features. This detailed information aids in property valuation and negotiation.
Land Management and Conservation
Land managers use LandWatch maps to monitor land use changes, track deforestation or habitat loss, and plan conservation efforts. The visualization of ecological features facilitates informed conservation strategies.
Agricultural Planning and Development
Farmers and agricultural planners use LandWatch maps to assess soil types, identify suitable areas for cultivation, and optimize irrigation strategies. This leads to improved crop yields and efficient resource management.
Environmental Impact Assessments
Environmental impact assessments rely on LandWatch maps to analyze potential environmental impacts of development projects. The maps help identify sensitive ecosystems, assess potential risks, and develop mitigation strategies.
Diverse Applications Across Industries
- Urban planning and development
- Infrastructure planning and development
- Disaster response and recovery
- Insurance risk assessment
- Mining and resource exploration
Visual Representation and User Experience
The visual design and user experience of LandWatch maps significantly impact their usability and effectiveness. A well-designed interface enhances data interpretation and decision-making.
Visual Design and Layout
The visual design should prioritize clarity and ease of navigation. A clean layout, consistent color schemes, and clear labeling of features are essential. The ability to customize map display, such as changing basemap styles or highlighting specific data layers, enhances user control and efficiency.
User-Friendliness and Intuitiveness
The interface should be intuitive, even for users with limited mapping experience. Familiar map controls, clear tooltips, and responsive design across devices are crucial for a positive user experience. Comprehensive help documentation and tutorials can further improve user understanding.
Suggestions for Improvement
Enhanced customization options, including the ability to create and save custom map views, would increase user efficiency. Improved search functionality, perhaps incorporating natural language processing, could enhance the user experience. Integration with other data sources and tools could also improve functionality.
Comparison with Other Mapping Platforms
Comparison with other platforms should focus on aspects such as map clarity, search functionality, data visualization, and overall ease of use. User reviews and feedback from other platforms can provide valuable insights.
User Feedback on LandWatch Map Design and Functionality
| Aspect | Positive Feedback | Negative Feedback | Suggestions for Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Search Functionality | Easy to use, comprehensive results | Limited filtering options | Add more granular filtering capabilities |
| Data Visualization | Clear and concise data presentation | Some data layers difficult to interpret | Improve data layer labeling and symbology |
| User Interface | Intuitive and easy to navigate | Some features are not clearly labeled | Improve tooltips and documentation |
Future Developments and Improvements
Continuous improvement and innovation are vital for LandWatch maps to remain a leading resource for land-related information.
Areas for Improvement
Improved data integration, incorporating more diverse data sources, would enhance the map’s comprehensiveness. Advanced analytics capabilities, allowing users to perform spatial analyses and generate reports, would add significant value. Enhanced mobile accessibility and offline functionality would broaden the map’s usability.
Integration of New Data Sources
Integration with real-time data sources, such as weather data, traffic information, and environmental sensors, could provide a more dynamic and comprehensive view of land characteristics. Incorporating user-generated content, such as crowd-sourced observations, could enhance data richness.
Features Enhancing User Experience
Improved collaboration features, allowing multiple users to share and edit maps simultaneously, would enhance teamwork. The ability to create custom reports and export data in various formats would facilitate efficient data management. Personalized map views, tailored to individual user preferences, could further enhance the user experience.
Technology Advancements Improving Accuracy and Efficiency
Advancements in remote sensing technology, such as high-resolution satellite imagery and LiDAR data, can significantly improve the accuracy of map data. Artificial intelligence and machine learning can automate data processing and analysis, increasing efficiency and reducing errors.
Potential Future Developments
- Integration with virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies
- Development of advanced analytical tools for spatial data analysis
- Implementation of predictive modeling capabilities for land use change
- Improved accessibility for users with disabilities
Illustrative Example: A Hypothetical Property Search
This section details a hypothetical property search using LandWatch maps, illustrating the process and potential outcomes.
Searching for a Specific Property Type
Let’s imagine a search for a rural property suitable for agricultural use, with at least 100 acres, located within a specific county. The user would begin by entering the county name into the search bar. Then, they would utilize filtering options to specify property type (“agricultural”), minimum acreage (100 acres), and potentially other criteria such as proximity to roads or water sources.
The results would display properties matching these criteria, along with relevant information.
Identifying Property Boundaries, Acreage, and Nearby Features
Once a potential property is identified, the user can click on it to view detailed information. The map would clearly display the property boundaries, indicating the exact acreage. Additional data layers, such as topography, roads, and waterways, would be visible, allowing the user to assess the property’s location, accessibility, and suitability for their needs.
Informed Decision-Making in Land Acquisition, Landwatch map
This hypothetical scenario demonstrates how LandWatch maps support informed land acquisition decisions. By visualizing property boundaries, assessing acreage, and analyzing surrounding features, potential buyers can make informed decisions based on accurate and comprehensive data. This helps minimize risk and maximizes the chances of a successful land acquisition.
LandWatch Map represents a significant advancement in accessible land data management. Its comprehensive features, coupled with an intuitive interface, empower users to make informed decisions based on accurate and readily available information. While acknowledging inherent limitations in any GIS system, the platform’s ongoing development promises even greater accuracy, functionality, and user experience in the future. LandWatch Map stands as a valuable tool for navigating the complexities of land ownership, management, and planning.


